Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
In the world of thermal management, the selection of a Finned Tube Heat Exchanger can significantly impact system efficiency and performance. As industry expert Dr. John Smith, a renowned engineer in heat transfer technology, once stated, "The right heat exchanger can be the difference between an optimal system and one that struggles under poor performance." This highlights the crucial role that careful selection plays in ensuring effective heat exchange processes.
Choosing a Finned Tube Heat Exchanger involves a multitude of considerations, from design features to operational requirements. Factors such as fluid types, flow arrangements, and thermal load conditions must be meticulously evaluated to ensure the exchanger functions at its peak. With varying designs and configurations available, an informed approach to selection can lead to enhanced energy savings and improved system reliability.
As industries continue to prioritize efficiency and sustainability, understanding the principles behind selecting the appropriate Finned Tube Heat Exchanger is more important than ever. This guide will delve into ten essential tips that will aid in making an informed choice, ultimately leading to superior thermal performance and enhanced operational success.

Finned tube heat exchangers are critical components in various industrial applications, designed to enhance heat transfer efficiency by increasing the surface area for heat exchange. Understanding the basics of these systems is vital when it comes to selecting the right one for your needs. These devices typically consist of tubes with extended surfaces, known as fins, which facilitate the transfer of heat between a fluid in the tubes and a surrounding medium, often air or another fluid. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global market for heat exchangers is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% from 2021 to 2026, demonstrating the increasing reliance on efficient thermal management systems in various sectors.
When choosing a finned tube heat exchanger, it’s essential to consider factors such as the operating environment, fluid types, and required thermal performance. The thermal efficiency of finned tube heat exchangers can vary significantly based on fin design, spacing, and material. For instance, a study published in the International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer highlights that integrating optimized fin configurations can improve heat transfer rates by up to 30%, emphasizing the importance of tailored designs for specific applications. Understanding these fundamental concepts ensures that engineers and procurement professionals make informed decisions, leading to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced energy costs in their processes.
When it comes to the efficiency and performance of finned tube heat exchangers, several key factors must be considered. One of the most significant aspects is the surface area of the fins. According to industry reports, increasing the surface area can enhance the heat transfer efficiency by up to 50%. This is particularly crucial in applications where space is limited, as a compact design without sacrificing performance can lead to significant operational savings.
The choice of fin material also plays a critical role, with copper fins typically offering better thermal conductivity compared to aluminum, leading to improved overall effectiveness.
Another important factor is the flow arrangement within the heat exchanger. Counterflow configurations often yield a higher temperature differential, allowing for more efficient heat transfer. Research from the Heat Exchange Institute indicates that optimizing flow paths can reduce pressure drops and enhance thermal performance, which can translate to energy savings of approximately 10-15%. Furthermore, regularly maintaining and cleaning the heat exchanger can prevent fouling, which, if left unaddressed, can decrease efficiency by 20% or more. Therefore, understanding and implementing these factors can significantly impact the selection and long-term performance of finned tube heat exchangers in various industrial applications.
When selecting a finned tube heat exchanger, one of the crucial aspects to consider is the materials used in its construction. The choice of material affects not only the efficiency of heat transfer but also the durability and longevity of the exchanger in various operating environments. Common materials include copper, aluminum, and stainless steel, each offering distinct advantages and drawbacks.
For instance, copper provides excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring high thermal efficiency, while aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making it suitable for outdoor installations.
Another key consideration is the compatibility of the chosen materials with the working fluids and the operational conditions.
Corrosion resistance should be a top priority, especially in environments where fluids may contain aggressive chemicals or high levels of humidity. Stainless steel is often favored for its superior resistance to oxidation and corrosion, thereby enhancing the lifespan of the heat exchanger. It's also essential to evaluate factors such as thermal expansion, which can lead to material fatigue and failure over time. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of the application and operational conditions will guide the selection of the most appropriate materials for a reliable and efficient finned tube heat exchanger.
When selecting a finned tube heat exchanger, it is crucial to consider sizing and design parameters that significantly impact its efficiency and performance. One of the primary considerations is the heat transfer area, which should be calculated based on the specific thermal load requirements of your application. Ensuring that the exchanger has an adequate surface area facilitates optimal heat exchange between the fluids. In addition to surface area, the spacing and geometry of the fins play a vital role in enhancing the heat transfer rate. Properly designed fins increase the contact surface, thereby improving efficiency without necessitating a larger footprint.
Another key aspect of sizing is the flow arrangement of the fluids within the heat exchanger. Counterflow designs generally provide better thermal efficiency compared to parallel flow configurations, as they allow for a greater temperature differential. Further, the fluid velocities must be optimized to prevent issues such as fouling and pressure drop, which can adversely affect performance. The selection of materials used in the construction of the heat exchanger will also influence its thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, especially in demanding environments. By carefully evaluating these design parameters, one can ensure that the finned tube heat exchanger meets the operational demands while achieving reliable and efficient heat transfer.
| Parameter | Description | Recommended Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Area | The total area available for heat transfer. | 100 m² | Depends on flow rate and temperature differences. |
| Fluid Type | Type of fluid being heated or cooled. | Water | Must consider properties like viscosity. |
| Flow Arrangement | Configuration of the fluids in the heat exchanger. | Counterflow | Offers better efficiency compared to parallel flow. |
| Finned Tube Material | Material used for tubes and fins. | Copper or Aluminum | Consider corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. |
| Fin Density | Number of fins per unit length of tube. | 10 fins/m | Higher density increases surface area. |
| Heat Transfer Coefficient | Efficiency of heat transfer. | 500 W/m²K | Varies with fluid properties and flow rates. |
| Operating Pressure | Pressure of the fluids during operation. | 1.5 MPa | Safety factors must be considered. |
| Connection Type | Type of connections at the ends of the exchanger. | Flanged | Ease of maintenance and inspection. |
| Size and Dimensions | Overall dimensions of the heat exchanger. | 2m x 1.5m x 1m | Should fit into existing spaces efficiently. |
| Maintenance Access | Ease of accessing for inspection and repairs. | Good accessibility | Design to allow space for maintenance. |
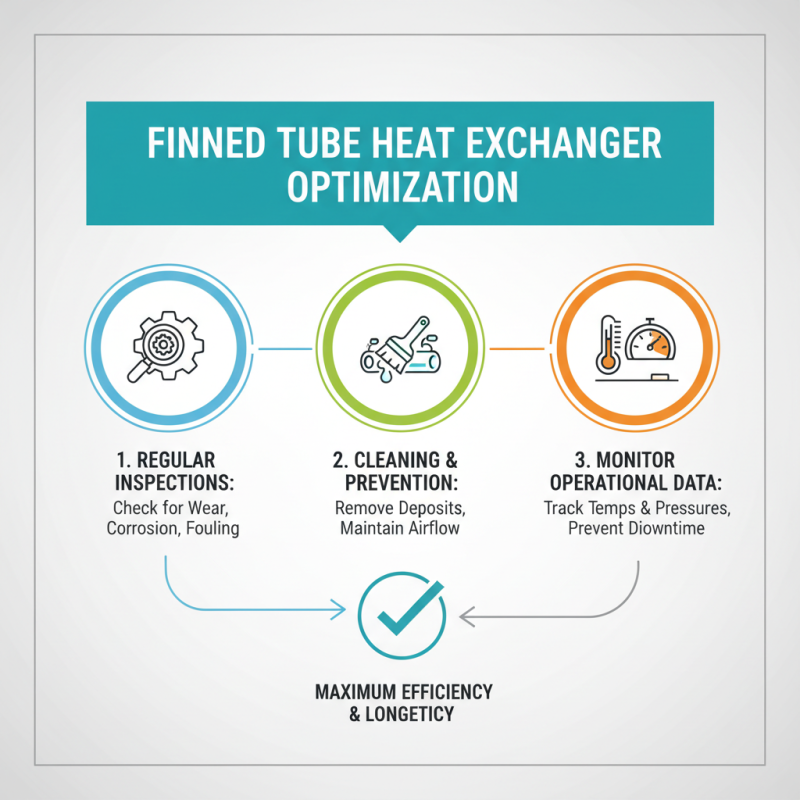
When it comes to maximizing the efficiency and longevity of finned tube heat exchangers, proper maintenance and operational practices are crucial. Regular inspections should be scheduled to identify any signs of wear, corrosion, or fouling early on. Cleaning the fins and tubes helps prevent the buildup of unwanted deposits that can hinder performance. Operators should monitor the fluid temperatures and pressures closely, as significant deviations can indicate that maintenance is required to rectify underlying issues and prevent costly downtime.
Additionally, ensuring that the heat exchanger is operating within its designed parameters is essential. Operators should familiarize themselves with the manufacturer's guidelines regarding operational limits and make necessary adjustments to avoid overloading the equipment. Implementing a routine lubrication schedule for any moving parts and ensuring proper sealing and insulation can also enhance efficiency. Training personnel to recognize operational anomalies and respond swiftly can make a significant difference in the heat exchanger’s reliability and efficiency. Overall, proactive maintenance and vigilant operational practices are key to ensuring optimal performance and extending the life of finned tube heat exchangers.