Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
Choosing the right heating air system for your home is a crucial task that can significantly affect your comfort and energy efficiency. According to renowned HVAC expert John Smith, “Selecting an appropriate heating air system is not just about keeping warm; it’s about creating a sustainable living environment that meets your family’s needs.” With so many options available, it can be overwhelming to determine which system will best suit your specific requirements.
When evaluating heating air systems, homeowners must take into account various factors such as the size of their space, energy efficiency ratings, and budget. Each system—whether it be a furnace, heat pump, or radiant heating—has unique features and benefits that can influence your decision. Tailoring your choice to your home’s characteristics and your lifestyle will ensure optimal performance and comfort throughout the colder months.
In this guide, we will explore the essential criteria to consider when selecting a heating air system for your home. By understanding your options and the implications of each choice, you can make an informed decision that not only enhances indoor comfort but also promotes energy efficiency and reduces long-term costs.

When selecting a heating air system for your home, there are several critical factors to consider, primarily to ensure energy efficiency and comfort. According to the Department of Energy, nearly half of a typical household's energy budget goes toward heating and cooling. Thus, opting for an energy-efficient system can significantly lower your overall bills and reduce your carbon footprint. Look for systems that carry the ENERGY STAR label, which signifies that they meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the EPA.
Another essential factor is the size of the system. An oversized unit may lead to frequent cycling and inefficient energy use, while an undersized system will struggle to maintain the desired temperature, thereby increasing wear and tear. The Manual J calculation, a standard recommended by the Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA), can help homeowners determine the appropriate size by taking into account various home characteristics, such as square footage, insulation quality, and window types. Furthermore, don’t overlook the importance of maintenance and warranty; a reliable heating air system backed by a solid warranty can provide peace of mind and longevity.
When it comes to choosing a heating air system for your home, understanding the pros and cons of different types is crucial.
The most common systems include central heating, heat pumps, and space heaters.
Central heating, often powered by gas or electricity, provides uniform warmth across large areas; however, installation costs can be significant, often ranging between $2,500 to $7,500, according to the Department of Energy.
On the positive side, central systems offer high efficiency and improved air quality with proper filtration.
Heat pumps, which leverage electricity to transfer heat, are gaining popularity due to their versatility and eco-friendliness.
They can provide both heating and cooling, making them a worthwhile investment, though upfront costs can be high—averaging around $5,000.
One downside is their performance can decline in extreme temperatures, which may require supplementary heating systems.
Tips: When selecting a heating system, consider the size of your home and the local climate.
A well-insulated home will drastically reduce energy costs regardless of the heating method chosen. Moreover, always look for Energy Star-rated systems to improve efficiency and save on long-term utility bills.
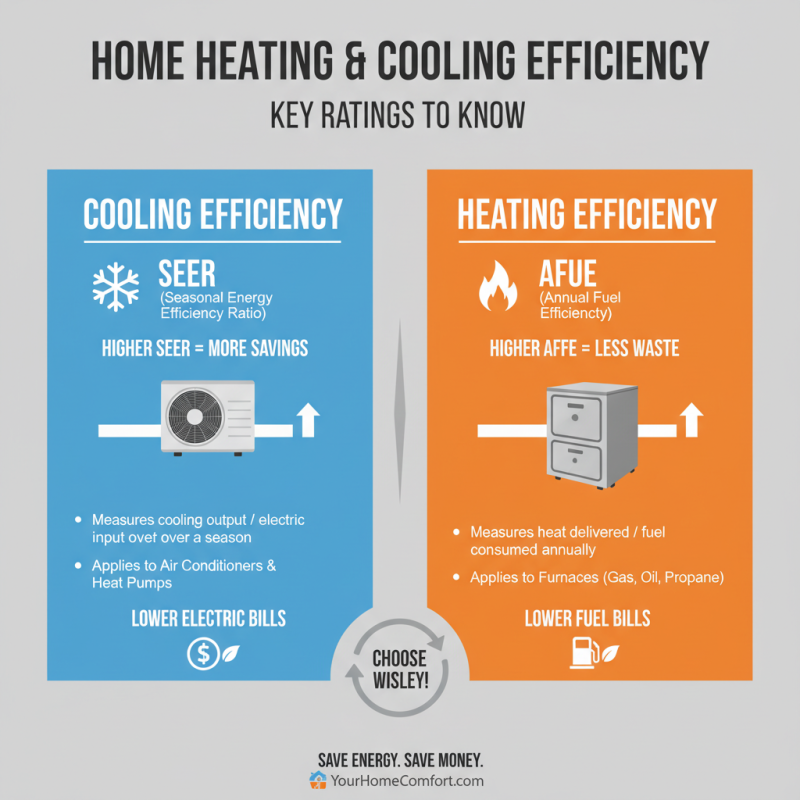
When selecting a heating air system for your home, understanding energy efficiency ratings is crucial. Two key metrics to consider are the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE). SEER measures the cooling output of an air conditioning system over a typical cooling season divided by the total electric energy input during that period. A higher SEER rating indicates greater efficiency, which can lead to substantial savings on energy bills.
On the other hand, AFUE is used for heating systems, indicating the percentage of fuel converted into heat within a year. For example, a furnace with an AFUE of 90% will convert 90% of the fuel it consumes into heat, while the remaining 10% is lost. Higher AFUE ratings suggest more efficient heating systems, making it essential to factor these ratings into your decision when choosing a heating air system. By evaluating SEER and AFUE, homeowners can make informed choices that align with both their comfort and energy savings goals.
When selecting a heating air system for your home, sizing the equipment properly is crucial for efficiency and comfort. According to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), an incorrectly sized system can lead to excessive energy use, higher utility bills, and insufficient heating. Ideally, a heating system should meet the home’s specific heating requirements, which can be derived from a Manual J calculation, a methodology endorsed by the Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA).
To ensure accurate sizing, consider factors such as your home’s square footage, insulation levels, and local climate. The DOE suggests that homes in colder climates may require systems with higher BTU capacity, while warmer areas can operate effectively with lower capacities. Furthermore, overly large systems can cycle on and off frequently, resulting in poor humidity control and temperature fluctuations.
Tips: Always consult with a qualified HVAC professional to perform a thorough assessment of your home’s heating needs. Additionally, invest in a programmable thermostat, which can help optimize the system's efficiency by adjusting the temperature based on your schedule. Lastly, regular maintenance is essential to ensure your system operates at its peak capacity, prolonging its lifespan and improving overall energy efficiency.
When selecting a heating air system, it is essential to factor in the installation and maintenance costs to ensure long-term affordability. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, the average cost of installing a new heating system ranges from $4,000 to $14,000, depending on the type and size of the system. This significant investment requires homeowners to meticulously plan their budgets. For instance, high-efficiency systems, while more expensive upfront, can save an average of 20% to 30% on energy bills over time. Therefore, it’s critical to evaluate not just the installation costs but also potential savings in ongoing energy expenses.
Maintenance is another crucial aspect that can influence overall costs. Data from the Air Conditioning Contractors of America indicates that regular system maintenance can extend the life of a heating system by up to 30%. Annual maintenance costs typically range from $100 to $300, which is a small price to pay compared to the potential repairs or replacements that could arise from neglecting the system. By investing in both installation and maintenance, homeowners can ensure efficient operation and longer system lifespan, effectively managing their budget in the long run.