Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
When it comes to optimizing thermal efficiency in various industrial applications, selecting the right Finned Tube Heat Exchanger is paramount. According to industry expert Dr. Emily Chen, a renowned thermal systems engineer, "The performance of a heat exchanger can significantly influence the overall efficiency and sustainability of a thermal system." Her insights underscore the importance of not only choosing a heat exchanger that meets technical specifications but also one that aligns well with the specific operational demands of the application.
Finned Tube Heat Exchangers are designed to enhance heat transfer between fluids, making them crucial in industries ranging from HVAC to chemical processing. With a multitude of designs, materials, and configurations available, the decision-making process can be complex. Factors such as fluid types, operational temperatures, and pressure conditions all play a critical role in determining the best fit. Each aspect must be meticulously evaluated to ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
In this article, we will explore the key considerations that should guide the selection of a Finned Tube Heat Exchanger for any application. By understanding the principles behind heat exchangers and the unique characteristics of various designs, engineers and procurement professionals can make informed decisions that enhance system performance and drive operational success.

Finned tube heat exchangers are essential components in various industrial applications, primarily designed to enhance heat transfer between fluids by maximizing surface area. These devices are particularly effective in situations where one fluid is significantly warmer or cooler than the other. According to the Global Heat Exchanger Market report, the demand for heat exchangers, including finned tube varieties, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2021 to 2027, driven largely by increasing energy efficiency requirements across industries.
The applications of finned tube heat exchangers are diverse, spanning sectors such as automotive, chemical processing, and power generation. Their design allows them to operate efficiently in environments with high heat transfer demands, such as cooling process gases or recovering heat from exhaust systems. A significant finding from the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) indicates that the use of finned tube heat exchangers can improve energy efficiency by as much as 30%, making them an attractive solution for manufacturers looking to reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Additionally, the adaptability of these heat exchangers to various working fluids, including steam and refrigerants, further underscores their versatility in meeting specific application needs.
When selecting a finned tube heat exchanger, understanding the heat transfer requirements specific to your application is crucial. Key industry parameters include the type of fluids involved, their temperatures, and flow rates. The thermal properties of these fluids, such as viscosity and specific heat, affect the heat transfer efficiency significantly. Additionally, the temperature difference between the hot and cold fluids is another critical factor in determining how well heat can be transferred through the exchanger.
Another important consideration is the design and construction of the heat exchanger itself, which should match the operational conditions of the application. Factors like the fin material and configuration greatly influence the surface area available for heat exchange, thereby affecting performance. Furthermore, assessing the required maintenance and the potential for fouling can help in choosing a design that minimizes operational inefficiencies while ensuring longevity. Evaluating these parameters effectively leads to a more tailored and efficient heat exchanger solution.
When selecting materials for finned tube heat exchangers, it is essential to consider the operational environment and the specific requirements of the application. Corrosion resistance is a primary concern, particularly in industries such as chemical processing or maritime operations, where exposure to aggressive fluids or saltwater can compromise the integrity of the heat exchanger. Common materials include stainless steel and special alloys that offer enhanced durability under harsh conditions. The choice of material should also take into account the temperatures and pressures involved in the process, ensuring that the material can withstand the operational stress without failure.
Another critical factor is thermal conductivity, which directly affects the efficiency of heat transfer. Materials with high thermal conductivity, like copper and aluminum, are often preferred for their superior performance, although they may not always provide the necessary corrosion resistance. In contrast, while materials like carbon steel might offer good strength and cost-effectiveness, they may require protective coatings to prevent rust and oxidation in humid environments. Ultimately, balancing these factors—corrosion resistance, thermal efficiency, and mechanical strength—will guide the selection of the most suitable material for a finned tube heat exchanger, enabling optimal performance in the intended application.
| Material Type | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Corrosion Resistance | Cost ($/kg) | Application Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 400 | Good | 6 | Ideal for low-temperature applications |
| Aluminum | 237 | Moderate | 3 | Lightweight and cost-effective for HVAC systems |
| Stainless Steel | 16 | Excellent | 15 | Suitable for high-temperature and corrosive environments |
| Titanium | 22 | Outstanding | 30 | Best for seawater and aggressive chemical environments |
| Carbon Steel | 60 | Fair | 2 | Cost-effective for non-corrosive applications |
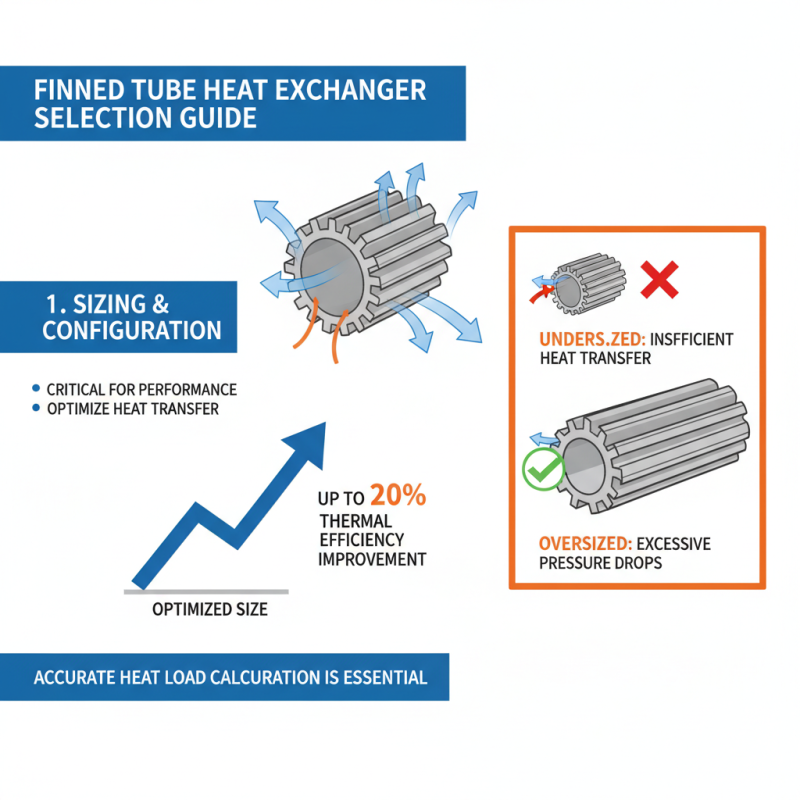
When selecting a finned tube heat exchanger, one of the primary considerations should be sizing and configuration options, which significantly influence performance. Proper sizing is critical, as undersized heat exchangers can lead to insufficient heat transfer, while oversized units may result in excessive pressure drops and increased operational costs. According to a recent industry report, optimizing the size of a heat exchanger can improve thermal efficiency by up to 20%, making it essential to accurately calculate the heat load requirements based on the specific application.
Configuration options, including the arrangement and type of fins, also play a vital role in enhancing performance. The choice between straight or spirally finned tubes can lead to differing levels of heat transfer efficiency and pressure drop. Data indicates that using spiral fins can enhance heat transfer rates by approximately 15% compared to cylindrical configurations, especially in systems with lower flow rates. Additionally, the spacing and angle of the fins affect how well the exchanger can manage fouling, impacting maintenance cycles and operation longevity. Therefore, leveraging these sizing and configuration strategies can lead to a more efficient and reliable heat exchange process tailored to the unique demands of an application.
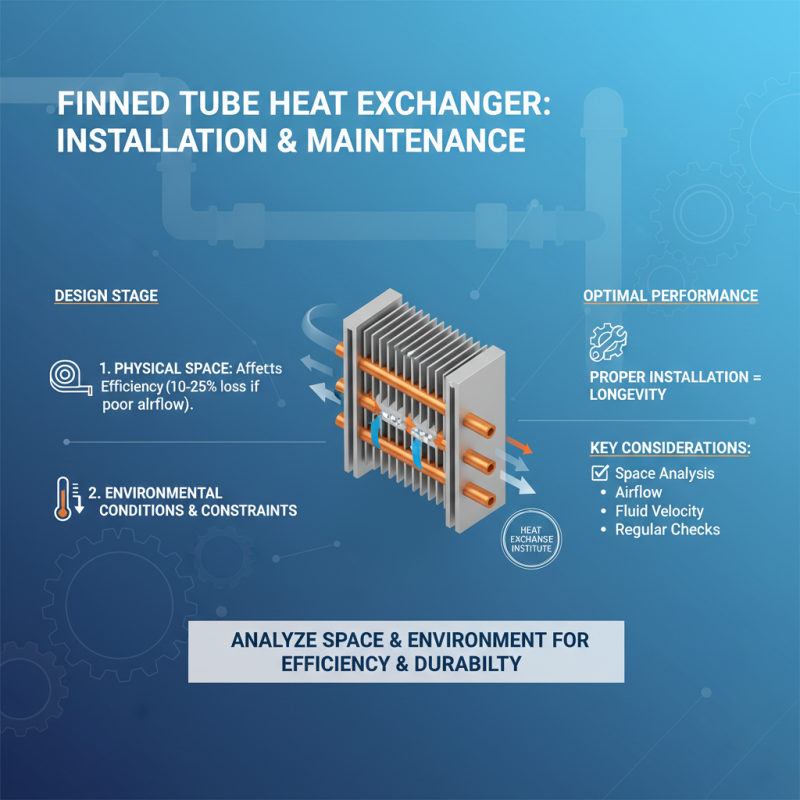
When selecting a finned tube heat exchanger, installation and maintenance considerations are critical to ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The design stage should account for the physical space available, which can significantly affect the heat exchanger's efficiency. According to the Heat Exchange Institute, inadequately designed installations can lead to a 10-25% reduction in thermal performance due to factors like poor airflow or insufficient fluid velocities. Therefore, it's essential to analyze the environmental conditions and spatial constraints before finalizing your choice.
Regular maintenance is vital for the effective operation of finned tube heat exchangers. Reports indicate that up to 30% of heat exchangers can experience efficiency losses due to fouling if not properly maintained. Routine cleaning and inspections not only prolong the equipment's lifespan but also enhance its reliability. Implementing a maintenance schedule with clear guidelines on frequency and methods can mitigate costly downtime and improve overall system performance.
Tip: Always assess the accessibility of the heat exchanger during installation. This will facilitate easier maintenance and inspections, helping to prevent any long-term operational issues. Additionally, consider using advanced materials with better resistance to fouling for enhanced durability.
Tip: Engage with a qualified technician during the design phase to understand the implications of the installation setup on maintenance strategies, as this will help in tailoring the heat exchanger performance to your specific application needs.