Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
In today's industrial landscape, choosing the right heating solution is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and reducing operating costs. Among various heating technologies, the Ceramic Band Heater stands out for its exceptional temperature control and durability, making it an essential component in industries such as plastics, food processing, and packaging. According to a recent market research report by Industry Insights, the demand for ceramic heating solutions has surged by over 15% in the last five years, indicating a growing recognition of their performance benefits compared to traditional heating methods.
Industry expert Dr. Jane Thompson emphasized the importance of selecting the appropriate Ceramic Band Heater for specific applications, stating, "The right ceramic heater can greatly influence the overall efficiency of a manufacturing process. Proper thermal management not only enhances product quality but also minimizes energy consumption." This highlights the critical role that a Ceramic Band Heater plays in maintaining optimal operational conditions while ensuring compliance with environmental standards.
As technology continues to advance, understanding the factors that influence the selection of Ceramic Band Heaters—such as watt density, insulation materials, and physical dimensions—becomes paramount. Making informed decisions can lead to significant improvements in process reliability and equipment longevity, thereby providing a competitive edge in a challenging market.

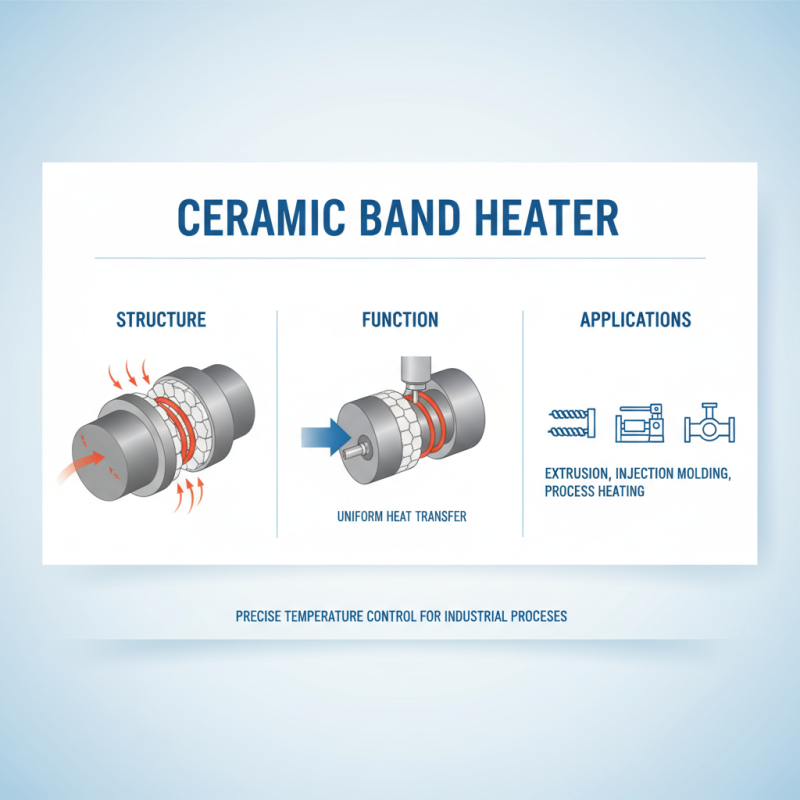
Ceramic band heaters are essential components in various industrial applications, primarily used for heating cylindrical objects. Understanding their basic structure and functionality is crucial for selecting the right heater for specific needs. These heaters consist of a ceramic insulating layer coupled with a heating element, allowing for efficient heat transfer while minimizing energy loss. Their design enables uniform heating around the surface of the object, making them ideal for processes involving extrusion, injection molding, and other manufacturing activities where precise temperature control is required.
The applications of ceramic band heaters are diverse, extending beyond traditional manufacturing to areas like food processing and pharmaceuticals. In these industries, maintaining specific temperatures is vital to ensure product quality and compliance with safety standards. Additionally, ceramic band heaters can withstand high temperatures and harsh environments, making them suitable for heavy-duty operations. Understanding the particular characteristics of the materials being processed, such as thermal conductivity and maximum temperature requirements, will aid in making informed decisions when selecting ceramic band heaters tailored to the intended application.

When selecting a ceramic band heater for industrial applications, several key factors should be considered to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with your specific needs. First and foremost, the heater's dimensions and wattage must align with the equipment it will be used with. Accurate measurements of the cylinder or pipe diameter will help determine the correct size of the heater, while the wattage indicates the heating capability. Insufficient wattage can lead to inefficient heating, whereas excessively high wattage could pose a risk of overheating and damage.
Another critical aspect to consider is the material compatibility of the heat band with the substances it will encounter. As ceramic band heaters can provide high temperatures, evaluating the operating environment, including temperature limits and potential exposure to corrosive materials, is essential. It's also important to consider the heater’s insulation properties, which can significantly affect energy efficiency and safety. Proper insulation reduces heat loss, enhances energy savings, and minimizes the risk of burns or heat-related injuries during operation.
Lastly, the durability and lifespan of the ceramic band heater should not be overlooked. Look for units designed for high operational cycles and those that can withstand thermal stress. This will ensure reliability and consistency in heating performance, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance costs over time. By carefully assessing these factors, you can choose a ceramic band heater that best fits your industrial heating requirements.
When selecting a ceramic band heater for industrial applications, understanding the differences among available types is crucial for optimizing performance and efficiency. Ceramic band heaters can vary in design, material composition, and application suitability. Common types include standard ceramic heaters, which are typically used in applications requiring moderate heating levels, and high-efficiency models that offer improved thermal performance and energy savings. The choice between these types often depends on the specific heating requirements of the machinery or process involved.
Another important distinction lies in the construction of the heaters. For instance, some ceramic band heaters feature a insulation layer to minimize heat loss, while others may have flexible designs to accommodate various sizes of equipment. Additionally, the watt density and operating temperature range are critical factors to consider; high-watt density heaters provide faster heating but require careful management to avoid overheating issues. Assessing these characteristics will help in selecting the right ceramic band heater that aligns with your industrial needs, ensuring effective and reliable heating solutions.
| Type of Heater | Temperature Range (°C) | Output Power (W) | Material | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Ceramic Band Heater | 0 - 350 | 250 - 1000 | Ceramic Insulation | Injection Molding |
| High-Temperature Ceramic Band Heater | 0 - 500 | 500 - 1500 | Silicone-Coated Ceramic | Plastics Processing |
| Flexible Ceramic Band Heater | 0 - 350 | 300 - 800 | Flexible Material | Non-Cylindrical Shapes |
| Low-Profile Ceramic Band Heater | 0 - 400 | 200 - 1000 | Ceramic and Metal | Compact Applications |
| Multizone Ceramic Band Heater | 0 - 300 | 400 - 1200 | High-Grade Ceramic | Complex Molding |
When selecting a ceramic band heater for industrial applications, it’s crucial to focus on the heater’s specifications and performance ratings to ensure optimal efficiency and longevity. Key specifications such as watt density, maximum operating temperature, and material composition directly impact the functionality of the heater. Industry reports indicate that heaters with a watt density of 30-60 watts per square inch are suitable for most applications, as they provide a balance between heat-up time and surface temperature. Additionally, the maximum operating temperature of the ceramic band heater should align with the requirements of your industrial processes, typically ranging from 100°C to 500°C, depending on the materials being heated.
Tips: Always assess the thermal conductivity of the materials used in the band heater’s construction. High-quality ceramics can significantly enhance heat transfer efficiency, leading to better performance and reduced energy costs. Moreover, look for performance ratings such as thermal cycling tests, which can give insights into the heater's durability and reliability under operational stresses.
Furthermore, consider the shape and size of the heater to ensure proper fit and compatibility with your equipment. Data from industry analytics suggest that a proper fit can improve heat distribution and minimize hotspots, which avoids unnecessary energy consumption. An optimal connection method is also essential, as secure and stable electrical connections enhance the heater’s performance while reducing the risk of failure during operation.
To ensure the longevity of ceramic band heaters, regular maintenance is essential. One effective practice is to keep the heater clean and free from contaminants. Dust, oils, and other residues can accumulate on the surface, which may affect performance and efficiency. Regularly wiping down the heater with a soft, dry cloth can prevent buildup, while ensuring the operating environment is clean can further enhance the heater's lifespan.
Another critical aspect of maintenance involves monitoring the operating temperatures and adjusting power settings as needed. Overheating can lead to premature failure of the heater components, so it's important to adhere to the manufacturer's recommendations regarding temperature limits. Implementing a routine inspection schedule to check for any signs of wear or damage can help catch issues early. Additionally, ensuring proper alignment and fitting during installation can prevent stress on the heater, allowing it to operate optimally for an extended period.